March 24, 2024, 9:38 AM IST
In our past two sessions, we discussed the Gastrointestinal Tract and the Respiratory System, which provide the nutrients and oxygen necessary for survival.
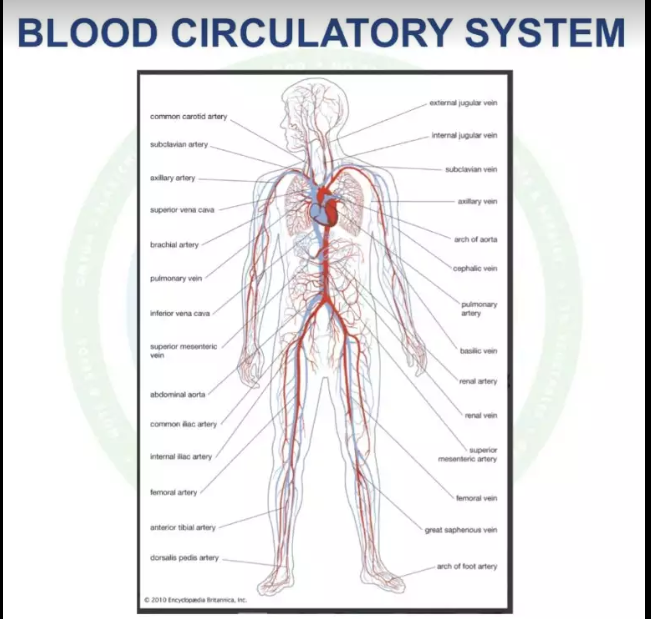
Once absorbed, these nutrients need to be transported to every part of the human body, a task accomplished by the blood circulatory system.
This system is comprised of a heart that acts as a pump and approximately 70,000 miles of blood vessels, evenly split between arteries (which carry blood from the heart to all body parts) and veins (which return the blood to the heart). At the site where the blood is delivered, these vessels narrow into thin capillaries.
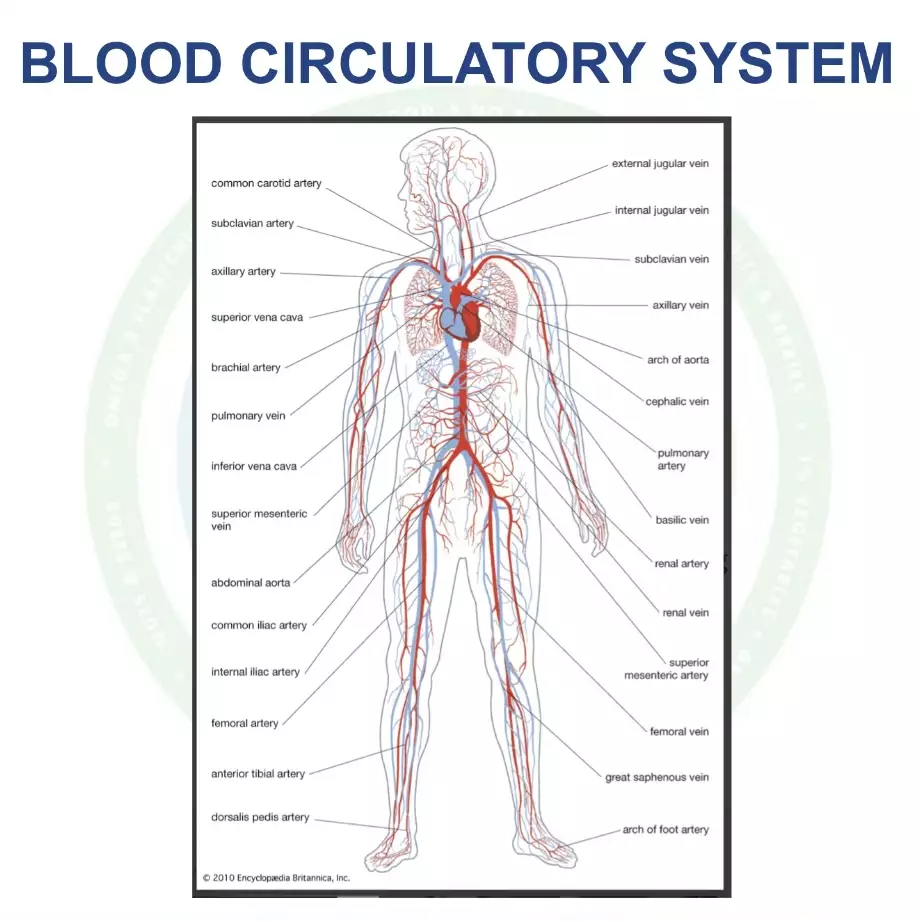
The blood vessels’ internal lining consists of a single layer of endothelial cells. This network is so extensive that the total surface area of this lining equals about 6-8 tennis courts. Collectively, this surface is known as the endothelium, arguably the largest organ in the human body. When the heart pumps blood, it causes the blood vessels to expand slightly due to pressure, which then drops, causing the vessels to shrink. These fluctuations are known as systolic and diastolic blood pressures.
Nitric Oxide Gas
A unique feature of the endothelial lining is its ability to release nitric oxide (NO) gas, facilitating smooth blood flow. When blood vessels develop plaque, the effective opening narrows, increasing the friction and, consequently, the blood pressure needed to maintain blood flow.
Evolution Time Line
Our bodies have evolved over billions of years. In a hypothetical 500-page book about human evolution, the domestication of animals and the advent of agriculture would appear only in the last paragraph of the final page. I mention this to address common arguments advocating animal-based foods, despite the facts.
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is the body’s reaction to perceived threats, which may not always be genuine. For instance, consider everyday activities that pose no danger because they are familiar. When we rise early in the morning, there are numerous routines we follow that do not alarm us because they are habitual, and we recognize the individuals involved. For instance, a sweeper cleans the street, a newspaper delivery person brings the newspaper, and the regular housekeeper rings the doorbell, to which we respond by letting her in.
Imagine a scenario where the doorbell rings again, and through the peephole, you see a tall, unfamiliar figure. This might trigger a sense of alarm or perceived threat. You might whisper to your spouse to stay silent, pretending no one is home, in hopes the stranger will leave. Alternatively, if your spouse is a retired military officer, he might retrieve a firearm from a safe and loudly inquire who’s at the door. There could be various responses to this situation. The individual outside may pose no actual threat and could be a new neighbor seeking directions to the university. Nonetheless, the critical point here is the perception of threat and the consequent reaction, which is analogous to inflammation. In this metaphor, the situation is inflammatory, prompting an ‘inflamed’ response, which represents inflammation.
Inflammatory Foods
Consuming plant-based whole foods, which have been part of our diet for millions of years, does not alarm the body. However, introducing animal products, refined, or ultra-processed foods, which are relatively new to our diet, triggers an inflammatory response. Such foods can compromise the integrity of the endothelial lining, leading to the formation of plaques as a repair mechanism.
Atherosclerosis
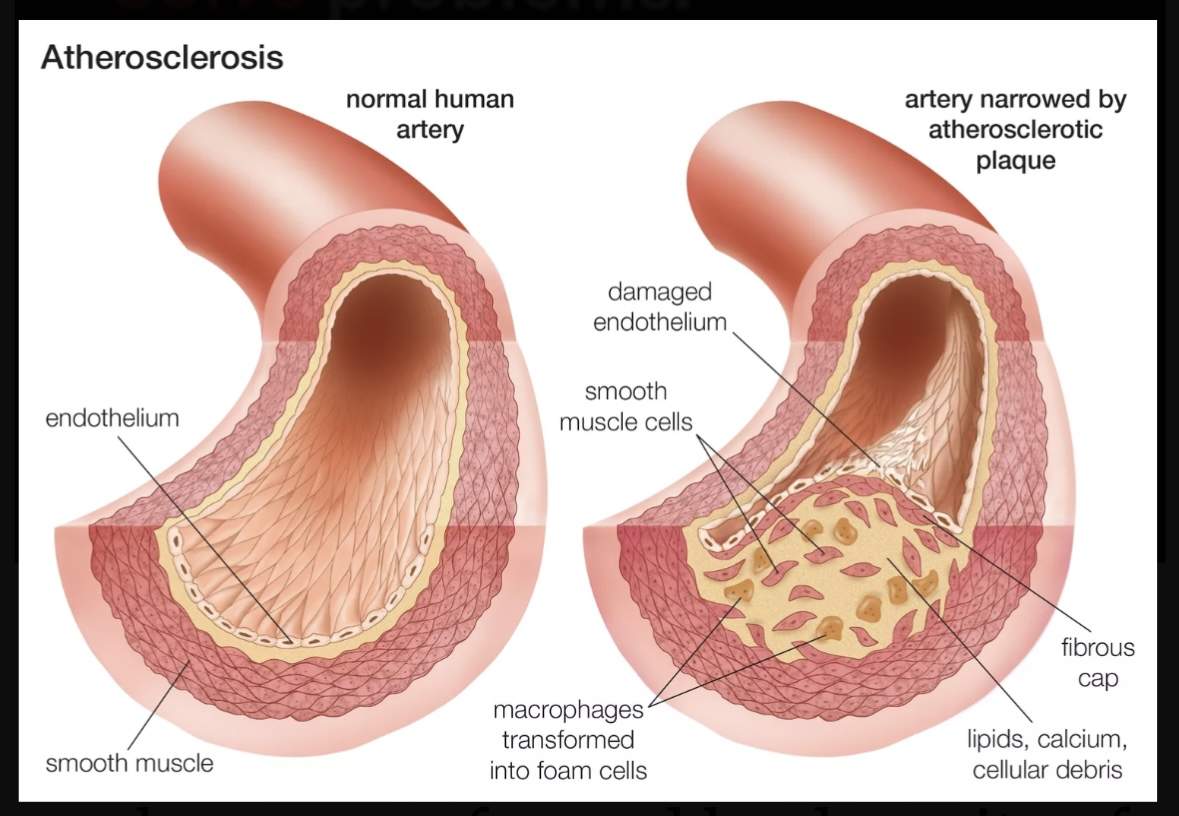
This process is called atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis starts early, as soon as children transition from breast milk to solid foods. Continuous consumption of inflammatory foods promotes plaque buildup, narrowing blood vessels and leading to increased blood pressure, hypertension, and other cardiovascular diseases. Atherosclerosis is a leading cause of death in the US and likely worldwide.
Green leafy vegetables to the rescue
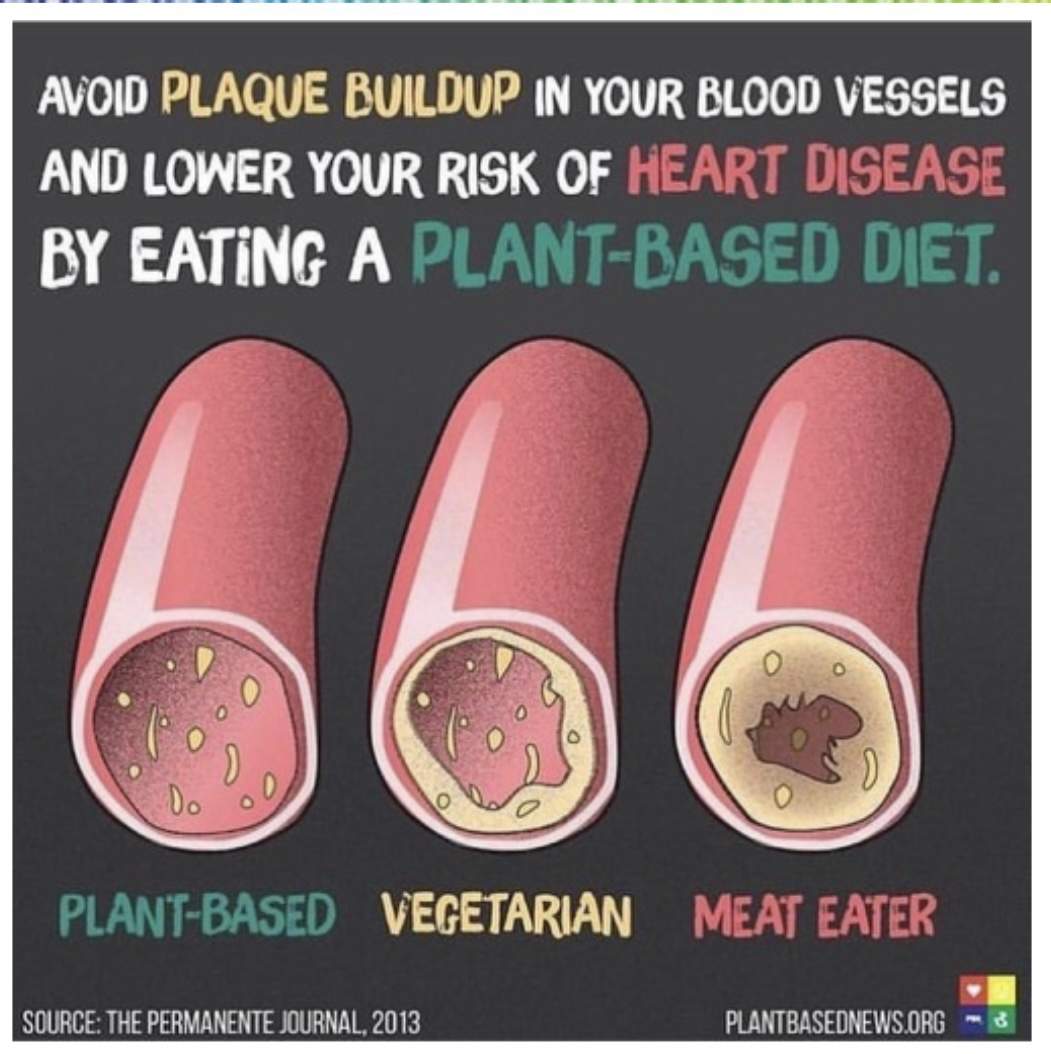
Green leafy vegetables are very rich in nitrates. When we consume them as salads or green juice, they release nitric oxide in the blood, helping unclog the blood vessels. This effect has been demonstrated by Dr. Caldwell Esselystyn of the Cleveland Clinic and Dr. Dean Ornish of UCSF, showing potential in reversing cardiovascular diseases and reducing dependency on medications.
One must understand that lifestyle diseases are not random phenomena and they do not develop all of a sudden. They exist on a continuum and the markers like BP are body’s way of compensating for them. Lowering the markers with medication whether Allopathic, Homeopathic, Unani or Ayurvedic is not the solution. One must address the cause which is almost always our diet and lifestyle.
Lymphatic system
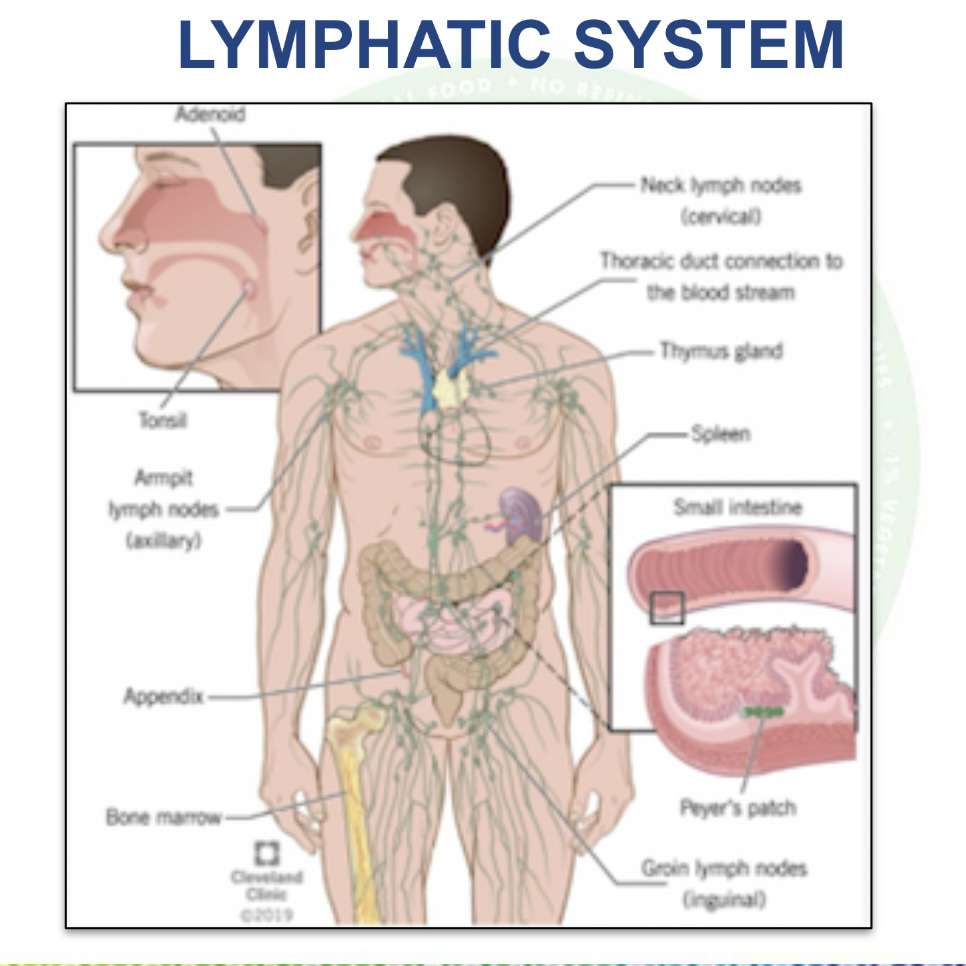
So far we have discussed how nutrients, essential for life, are consumed and distributed throughout the body. With the help of these nutrients every cell performs its metabolic function and in the process creates waste. The gaseous waste carbon dioxide is removed by the respiratory system but other waste is excreted as sweat, urine and feces. The system that collects this waste and takes it to the organs that excrete it (kidney, colon and skin) is called the Lymphatic System. It consists of a large network
The lymphatic system is also part of the immune system. It keeps body fluid levels in balance and defends the body against infections. The way the lymphatic system functions is by removing fluids (other than blood) from body tissues and cleaning it and recycling it.
Many of the lymph nodes reside in our underarms and where our legs join the body. Interestingly the lymphatic system does not have a pump and relies heavily on the body’s movement specially the hands and the legs.
This is one reason why the regular movement of hands and legs is very important. The important function of walking is often neglected by most writers while criticizing the 10,000 steps recommendation. Ideally these steps should be spread throughout the day as much as possible.
With this discussion, we’ve covered four critical systems of human physiology. Next week, we’ll delve into the basics of nutrition.
To Read this article on Times of India click here

Share and get 15% off!
Simply share this product on one of the following social networks and you will unlock 15% off!